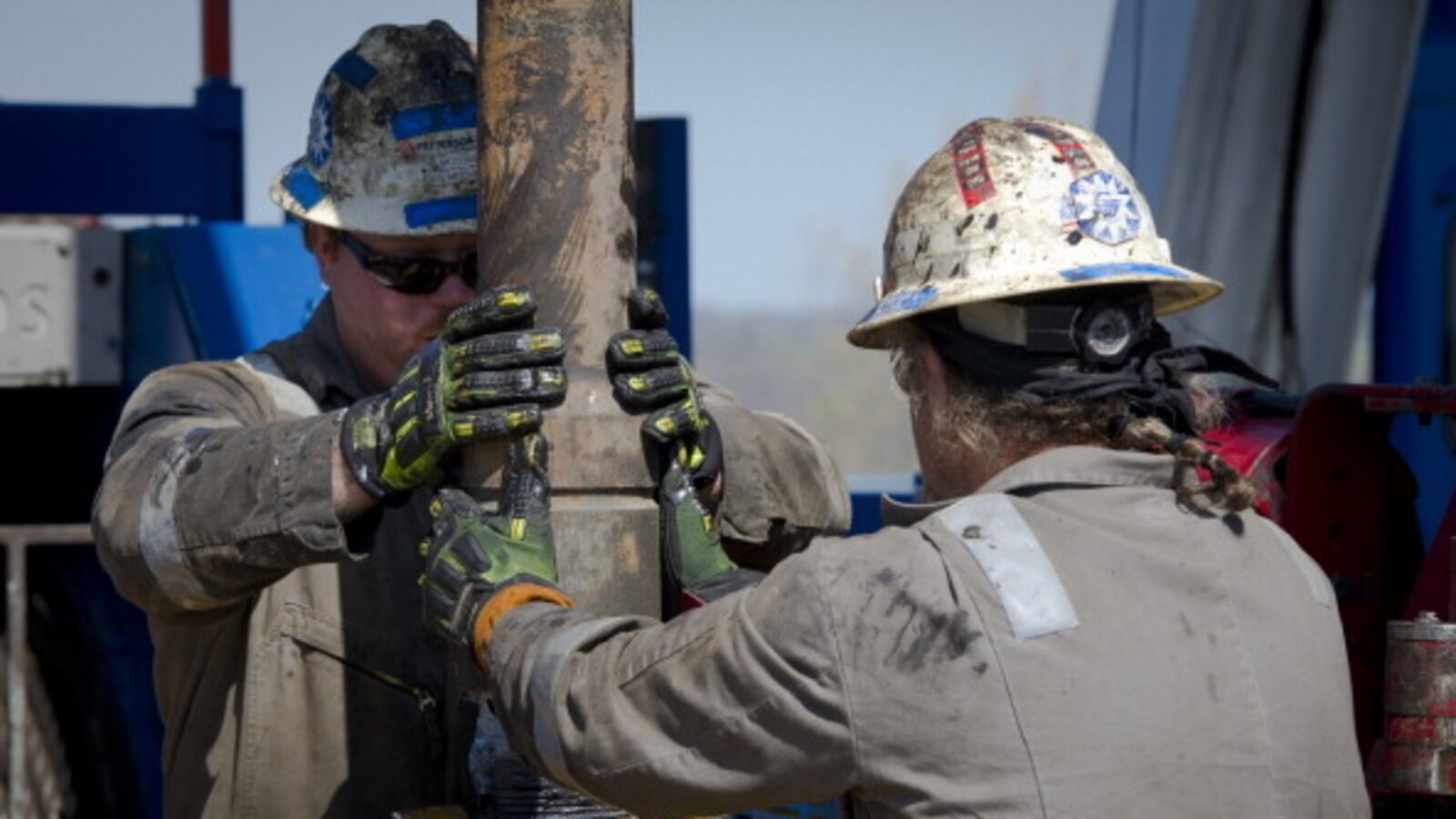
One of the unsung innovations in energy extraction is the ability to retrieve shale gas out of tight rock formations. It is cleaner than coal, and thanks to its abundance, natural gas prices have gone down significantly.
The Associated Press reports on a stunning result of this: America's carbon emissions have been reduced to levels not seen since 1992.
PITTSBURGH (AP) — In a surprising turnaround, the amount of carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere in the U.S. has fallen dramatically to its lowest level in 20 years, and government officials say the biggest reason is that cheap and plentiful natural gas has led many power plant operators to switch from dirtier-burning coal.
Many of the world's leading climate scientists didn't see the drop coming, in large part because it happened as a result of market forces rather than direct government action against carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere.
Michael Mann, director of the Earth System Science Center at Penn State University, said the shift away from coal is reason for "cautious optimism" about potential ways to deal with climate change. He said it demonstrates that "ultimately people follow their wallets" on global warming.
"There's a very clear lesson here. What it shows is that if you make a cleaner energy source cheaper, you will displace dirtier sources," said Roger Pielke Jr., a climate expert at the University of Colorado.
In a little-noticed technical report, the U.S. Energy Information Agency, a part of the Energy Department, said this month that energy related U.S. CO2 emissions for the first four months of this year fell to about 1992 levels. Energy emissions make up about 98 percent of the total. The Associated Press contacted environmental experts, scientists and utility companies and learned that virtually everyone believes the shift could have major long-term implications for U.S. energy policy.
...
A frenzy of shale gas drilling in the Northeast's Marcellus Shale and in Texas, Arkansas and Louisiana has caused the wholesale price of natural gas to plummet from $7 or $8 per unit to about $3 over the past four years, making it cheaper to burn than coal for a given amount of energy produced. As a result, utilities are relying more than ever on gas-fired generating plants.
The AP also notes the irony that this achievement was done largely via market forces as opposed to international climate-change treaties:
Mann called it "ironic" that the shift from coal to gas has helped bring the U.S. closer to meeting some of the greenhouse gas targets in the 1997 Kyoto treaty on global warming, which the United States never ratified. On the other hand, leaks of methane from natural gas wells could be pushing the U.S. over the Kyoto target for that gas.
Even with such questions, public health experts welcome the shift, since it is reducing air pollution.
"The trend is good. We like it. We are pleased that we're shifting away from one of the dirtiest sources to one that's much cleaner," said Janice Nolen, an American Lung Association spokeswoman. "It's been a real surprise to see this kind of shift. We certainly didn't predict it."